Origins of the Name Horn of Africa
Origins of the names of the countries in the Horn of Africa; Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
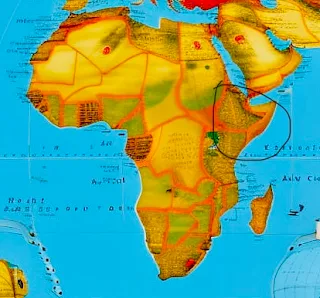
The Horn of Africa is a region in eastern Africa that resembles a horn on the map. It includes the countries of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia. The origin and meaning of this name is a fascinating topic in history. Some scholars believe that the name comes from the shape of the region, while others suggest that it refers to the horn-like ivory trade that flourished there in ancient times.
The Horn of Africa has a long and rich history of Etymology.
Etymology is the study of the origin and meaning of words, especially the names of places. It helps us understand how languages evolve, how words relate to each other, and how meanings change over time. Etymology enriches our vocabulary, enhances our communication skills, and deepens our appreciation of culture and literature. Etymology is cool.
One possible origin of the name Horn of Africa is from ancient Greek geographers, who called the region Keras Aithiopias, meaning Horn of Ethiopia. Ethiopia was a broad term used by the Greeks to refer to the lands south of Egypt, not necessarily the modern country of Ethiopia. The Greeks may have been influenced by the shape of the landmass, or by the presence of rhinoceroses in the region, which have horns on their noses.
Another possible origin of the name is from Arabic sources, who called the region al-Jazira al-Khadra, meaning the Green Island. This name may have been inspired by the contrast between the fertile coastal areas and the arid interior of the region. The Arabic term was later translated into Latin as Caput Viride, meaning Green Head or Green Cape, which may have been corrupted into Horn over time.
The name Horn of Africa has been used in English since at least the 19th century, and it is still widely used today to refer to this geopolitically and culturally important region. However, some people prefer to use other names for the region, such as the Somali Peninsula, or the Land of Punt.
How the countries of the Horn of Africa got their names.
The name Djibouti comes from the Afar word gabouti, which means a place where palm trees grow. The Afar are an ethnic group that inhabits parts of Djibouti, Ethiopia, and Eritrea. This country was formerly known as French Somaliland (1883-1967) and then as the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas (1967-1977), before gaining its independence from France in 1977 and adopting its current name.
The name Eritrea comes from the Greek word erythra thalassa, which means red sea. The Greeks called this region Erythraia after the reddish color of the water caused by algae blooms. This country was formerly part of the ancient kingdom of Aksum (c. 100-940 CE) and then part of the medieval realm of Medri Bahri (c. 1137-1879). It was later colonized by Italy (1890-1941) and then became part of Ethiopia (1952-1993), before declaring its independence in 1993.
The name Ethiopia comes from the Greek word aithiopia, which means land of burnt faces. The Greeks used this term to refer to the people living south of Egypt who had dark skin. Ethiopia was also known as Abyssinia, which comes from the Arabic word habashat, which means mixed.
This reflects the ethnic and cultural diversity of Ethiopia. This country was formerly known as Abyssinia (c. 1270-1974), which was derived from the Arabic name for the Habesha people who inhabited the region. It was also called Ethiopia by the ancient Greeks and Romans, which means land of burnt faces in Greek. It became a federal republic in 1974 after the overthrow of Emperor Haile Selassie.
The name Somalia comes from the Arabic word sumal, which means go well or be prosperous. The Arabs used this term to refer to the people living on the Somali coast who traded with them. Somalia was also known as Punt or Land of Punt by the ancient Egyptians, who obtained exotic goods such as frankincense, myrrh, and ivory from this region.
This country was formerly divided into several sultanates and kingdoms, such as the Ajuran Sultanate (13th-17th centuries), the Adal Sultanate (1415-1577), the Geledi Sultanate (17th-19th centuries), and the Dervish State (1896-1920). It was also colonized by Britain, Italy, and France, who divided it into British Somaliland (1884-1960), Italian Somaliland (1889-1960), and French Somaliland (1862-1977). Somalia became independent in 1960 after merging with former British Somaliland and former Italian Somaliland.